Global population trends are a critical area of study, providing valuable insights into the demographic shifts shaping our world. This article delves into population statistics and trends across all continents, from the densely populated regions of Asia and Africa to the diverse landscapes of Europe and the Americas, and the unique dynamics of Australia and Antarctica. By examining the varying growth rates, migration patterns, and demographic changes, we aim to offer a comprehensive overview of the current state of the world population. Understanding these trends is essential for addressing global challenges and planning for a sustainable future. Join us as we explore the fascinating and complex dynamics of population changes across the globe.
solaviral.com will lead a thorough examination of this topic.
1. Introduction
Global population trends are a critical area of study, providing valuable insights into the demographic shifts that shape our world. The dynamics of population changes across different continents reveal much about economic development, resource allocation, social structures, and environmental impacts. This article delves into population statistics and trends across all continents, from the densely populated regions of Asia and Africa to the diverse landscapes of Europe and the Americas, and the unique dynamics of Australia and Antarctica. By examining varying growth rates, migration patterns, urbanization trends, and demographic changes, we aim to offer a comprehensive overview of the current state of the world population. These insights are crucial for policymakers, researchers, and anyone interested in understanding how population dynamics influence global challenges such as climate change, economic inequality, and sustainable development. Join us as we explore the fascinating and complex dynamics of population changes across the globe, and gain a deeper understanding of the factors driving these trends.
2. Asia

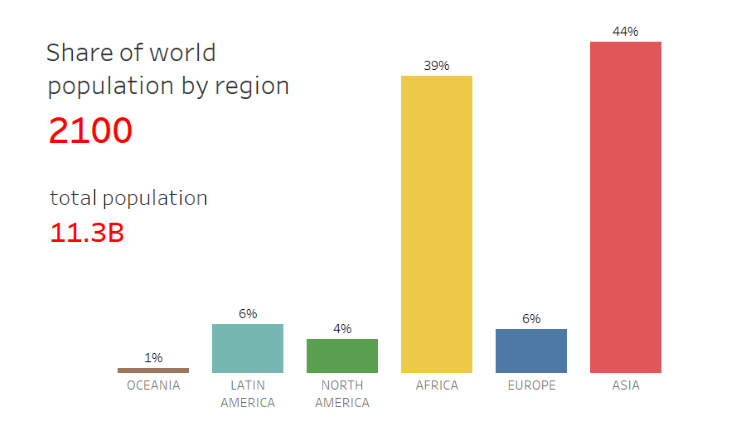
Asia, the world’s most populous continent, is home to over 4.7 billion people, accounting for approximately 60% of the global population. This vast and diverse region experiences significant demographic trends that have profound implications both locally and globally. Countries like China and India lead in population size, each surpassing a billion residents. Rapid urbanization is a defining feature, with megacities such as Tokyo, Shanghai, and Mumbai growing at unprecedented rates. Despite economic advancements, Asia faces challenges including aging populations in countries like Japan and South Korea, and youthful demographics in nations such as India and the Philippines. Migration, both within and across borders, further shapes the region’s demographic landscape. The continent’s population growth, coupled with economic development, exerts immense pressure on resources, infrastructure, and the environment. Understanding these dynamics is essential for addressing the unique challenges and opportunities presented by Asia’s population trends, from economic growth and labor markets to sustainability and social cohesion.
3. Africa
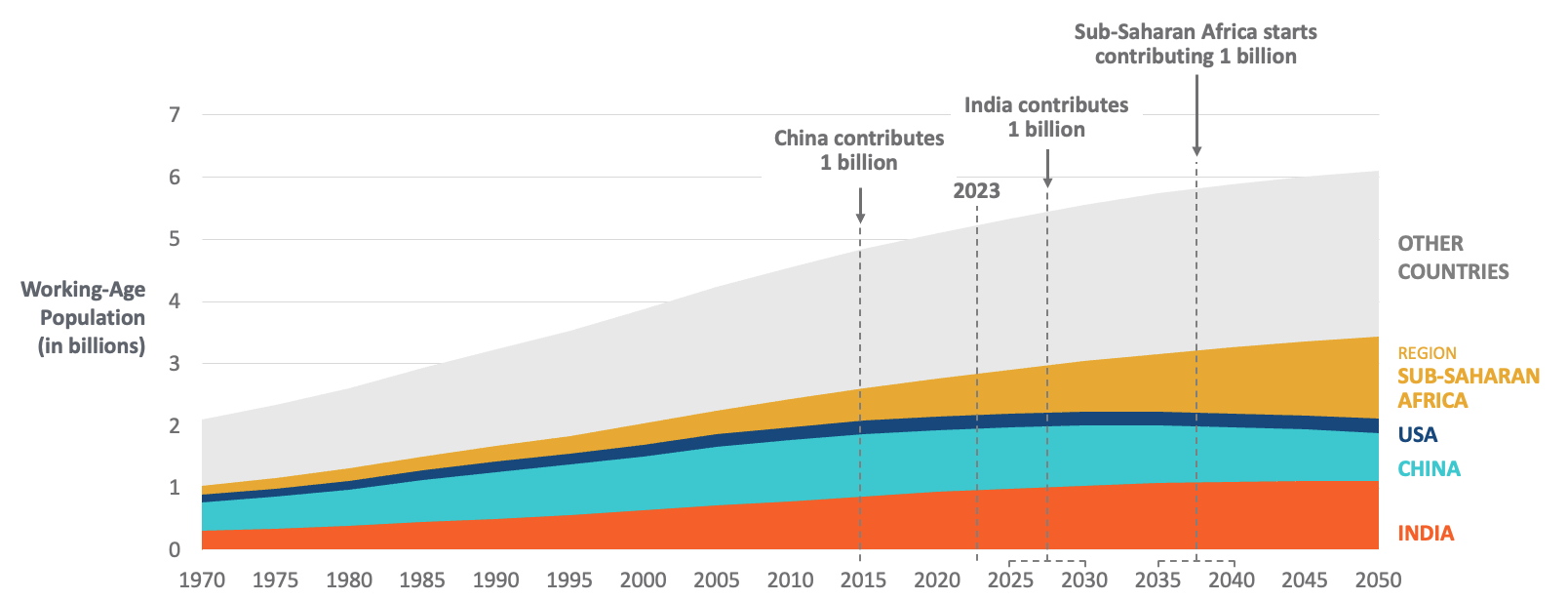
Africa is the second most populous continent, with over 1.3 billion people. The continent is characterized by rapid population growth, with some of the highest birth rates in the world. Countries like Nigeria, Ethiopia, and Egypt are at the forefront of this demographic surge. Africa’s youthful population presents both opportunities and challenges. A young workforce has the potential to drive economic growth, innovation, and development. However, high fertility rates and population growth also strain resources, healthcare, and education systems. Urbanization is another significant trend, with cities like Lagos, Cairo, and Nairobi expanding rapidly. Migration, both within the continent and to other regions, also plays a crucial role in shaping Africa’s demographic landscape. Additionally, the continent faces challenges related to poverty, disease, and political instability, which impact population dynamics. Understanding Africa’s population trends is vital for formulating policies that promote sustainable development, economic resilience, and social stability. The continent’s demographic future holds promise, provided these challenges are effectively managed.
4. Europe
Europe, with a population of approximately 746 million people, presents a unique demographic profile characterized by low birth rates, aging populations, and significant migration trends. Unlike other continents, Europe faces the challenge of declining populations in several countries, such as Germany, Italy, and Spain, where birth rates have fallen below replacement levels. This demographic shift is leading to an increasingly aging population, necessitating substantial adjustments in social policies, healthcare systems, and labor markets to support an older demographic.
Migration has become a crucial factor in Europe’s population dynamics. Influxes of migrants from Africa, the Middle East, and Asia have contributed to population growth in some regions, counterbalancing natural population decline. Cities such as Berlin, London, and Paris have become multicultural hubs due to significant immigrant communities. This migration influx brings diverse cultural influences but also presents challenges in terms of integration, social cohesion, and political response.
Urbanization continues to shape Europe’s demographic landscape, with major cities growing while rural areas face depopulation. The European Union’s policies on freedom of movement have facilitated intra-continental migration, contributing to economic disparities between regions.
Understanding Europe’s demographic trends is essential for addressing its unique set of challenges, from maintaining economic vitality and supporting aging populations to managing migration and fostering social integration. These dynamics will significantly influence Europe’s future in terms of economic stability, cultural identity, and political landscape.

5. North America
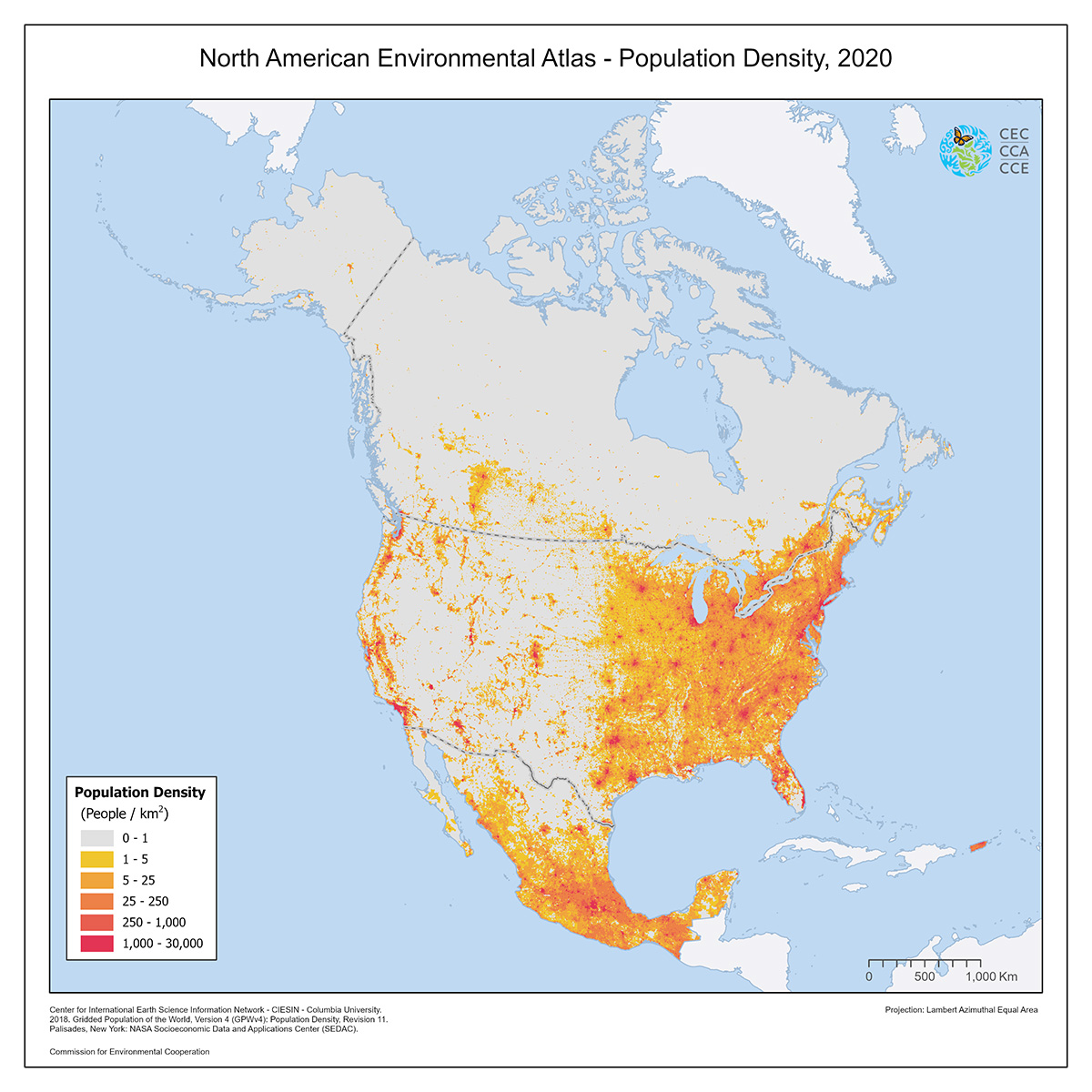
North America, comprising the United States, Canada, and Mexico, has a diverse population of approximately 600 million people. The continent’s demographic trends are shaped by a mix of natural population growth and significant immigration. The United States, the most populous country in the region, has a dynamic demographic profile characterized by a relatively high birth rate and substantial immigration, which contribute to its population growth and cultural diversity.
Canada, known for its welcoming immigration policies, also experiences population growth primarily driven by immigrants, who help offset the country’s lower natural birth rates. Mexico, with a younger population, faces different demographic challenges and opportunities, including urbanization and economic development.
Urbanization is a significant trend across North America, with major cities like New York, Los Angeles, Toronto, and Mexico City expanding rapidly. These urban centers are hubs of economic activity, cultural exchange, and innovation. However, they also face challenges related to infrastructure, housing, and environmental sustainability.
Migration plays a pivotal role in shaping North America’s demographic landscape. Both legal and undocumented immigration impact the social and economic fabric of the region. Understanding these trends is crucial for addressing policy issues related to immigration, urban planning, and social services, ensuring the region can sustainably manage its population growth and diversity.
6. South America
South America, home to over 430 million people, exhibits diverse demographic trends influenced by varying birth rates, migration patterns, and urbanization. Countries like Brazil and Argentina lead the continent in population size, each with unique demographic characteristics. Brazil, the most populous country, experiences moderate population growth and significant urbanization, with cities like São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro expanding rapidly.
Urbanization is a defining trend across South America, with a substantial portion of the population living in major cities. This rapid urban growth presents challenges, including infrastructure development, housing shortages, and environmental sustainability.
Migration also plays a significant role in shaping the continent’s demographics. Internal migration from rural areas to urban centers and international migration, particularly from neighboring countries facing economic or political instability, influence population dynamics.
South America’s youthful population presents both opportunities and challenges. A young workforce can drive economic growth, innovation, and social change. However, addressing issues such as education, employment, and healthcare is essential to harness this potential.
Understanding South America’s demographic trends is crucial for developing policies that promote sustainable development, social stability, and economic resilience in this diverse and dynamic region.
7. Australia
Australia, with a population of approximately 26 million, presents a unique demographic profile characterized by a high standard of living, significant immigration, and urbanization. The country experiences steady population growth primarily driven by immigration, as its natural birth rates remain relatively stable. Australia’s immigration policies attract people from diverse backgrounds, contributing to its multicultural society.
Urbanization is a prominent trend, with a significant portion of the population residing in major cities such as Sydney, Melbourne, and Brisbane. These urban centers are economic hubs, offering ample opportunities for employment, education, and cultural activities. However, the rapid growth of these cities also poses challenges, including housing affordability, infrastructure development, and environmental sustainability.
Australia’s demographic landscape is also influenced by internal migration patterns. People often move from rural areas to urban centers in search of better opportunities, further fueling urban growth. Additionally, Australia faces demographic challenges related to its aging population, necessitating adjustments in healthcare, social services, and workforce planning to support an older demographic.
Understanding Australia’s demographic trends is essential for policymakers and planners to address the unique challenges and opportunities presented by its population dynamics. By effectively managing immigration, urbanization, and aging, Australia can continue to thrive as a diverse, dynamic, and prosperous nation.
8. Antarctica
Antarctica, while not inhabited permanently by a native human population, hosts temporary scientific research stations year-round. These stations are operated by various countries and international organizations conducting scientific studies on the continent’s unique environment. The population of researchers and support staff fluctuates seasonally, typically peaking during the austral summer when conditions are more hospitable.
The demographic focus in Antarctica revolves around scientific research rather than traditional settlement. Researchers study climate change, glaciology, marine biology, and other fields crucial to understanding global environmental dynamics. Living conditions are challenging, with extreme cold, isolation, and logistical constraints posing significant challenges to daily life and scientific operations.
Despite its harsh environment, Antarctica serves as a crucial research platform, providing insights into global climate patterns and environmental changes that affect all continents. The temporary population of scientists and support personnel plays a vital role in advancing scientific knowledge and international cooperation in this remote and pristine wilderness.
9. Global Implications
The demographic trends observed across continents have far-reaching global implications that impact various aspects of society, economy, and the environment. Population growth, urbanization, and migration patterns shape regional and global dynamics, influencing economic development, social stability, and environmental sustainability.
One key global implication is the interconnectedness of demographic shifts with economic growth and labor markets. Regions experiencing rapid population growth, such as Asia and Africa, present opportunities for economic expansion but also face challenges in meeting infrastructure demands and providing adequate social services.
Migration trends, both within and across continents, contribute to cultural diversity and labor market dynamics globally. Countries experiencing demographic decline, like many in Europe, rely on immigration to sustain their workforce and support aging populations.
Environmental sustainability is another critical concern. Population growth and urbanization strain natural resources and contribute to environmental degradation, affecting climate change and biodiversity globally. Understanding these demographic dynamics is crucial for implementing policies that promote sustainable development, social equity, and resilience to global challenges.
By studying and addressing these global implications, policymakers, researchers, and communities can work towards a more balanced and sustainable future, ensuring that demographic trends contribute positively to global well-being and prosperity.
10. Conclusion
In conclusion, the study of global population trends reveals a complex tapestry of demographic dynamics across continents, each presenting unique challenges and opportunities. From the rapid growth in Asia and Africa to the aging populations in Europe and the demographic shifts in North and South America, understanding these trends is crucial for informed policymaking and sustainable development.
Urbanization, migration, and environmental sustainability emerge as common themes influencing global demographics. Urban centers continue to expand, posing challenges in infrastructure, housing, and resource management. Migration patterns shape cultural diversity and labor markets globally, while also posing integration challenges in destination countries.
Environmental sustainability remains a pressing concern, as population growth and urbanization strain natural resources and contribute to climate change.
Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts across borders, informed by data-driven policies that prioritize social equity, economic resilience, and environmental stewardship. By leveraging the insights gained from studying global population trends, we can strive towards a more balanced and sustainable future for all regions and populations worldwide.
solaviral.com